-
ADD:
5F, No.657-3, Zhongzheng Road, Xinzhuang District, New Taipei City 242, Taiwan -
TEL:
+ 886-2-2209-1343 -
FAX:
+ 886-2-2903-0754 -
E-mail:
sales@greenconn.com
-
ADD:
No. 22 Jingshan Road, Luotian Third Industrial Zone, Yanluo Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province, China -
TEL:
+ 86-755-2707-0050/1 -
FAX:
+ 86-755-2707-0056 -
E-mail:
sales@greenconn.com
-
ADD:
2003, 24 Wellesley Street West, Toronto, Ontario, M4Y 2X6 -
TEL:
+ 1-704-493-1478 -
E-mail:
sales@greenconn.com
Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board (BTB) connectors are used to accurately interconnect printed circuit boards (PCBs) in a stackable manner. They can accommodate various types of PCB orientations, relative distances, and space constraints to allow for design flexibility. In addition, multiple materials, plating finishes, and pitches are available to meet electrical and mechanical specifications. Depending on the purpose of the interconnect, connectors are further offered as high-speed, floating, or power. To achieve the desired performance, all the above should be considered when designing an interconnect system.
Board-to-Board Connector Types
Pin Headers
Pin headers (male) and female headers (socket) are used as a set. A male pin header consists of one or more rows of metal pins molded into a plastic base. Due to their simplicity, male pin headers are the most cost-effective.
Female Headers
Female headers are the sockets that male headers fit into. These connectors complete the design by allowing the PCBs to be easily connected and easily replaced should either of the headers become damaged.
Box Headers
Box header connectors are featured with a plastic shroud around the header. This helps guide the connectors during the mating process to avoid mating errors.
High-Speed Connectors
High-Speed Connectors are specifically designed with robust terminals and high-temperature resistance plastic to be used in industrial applications that require high-speed transmission. The unique contact structure allows it to maintain a steady impedance profile, which ultimately minimizes both the noise and signal loss over the connectivity, with a potential secure data transmission of up to 4Gbps.
What are the orientation options for connectors?
PCB orientation is the relative position of two PCBs to be connected by BTB connectors. Here are some of the common orientations of BTB connectors:
In order to cater various PCB orientations (Parallel, Horizontal, Perpendicular), board-to-board connectors have been developed in straight, right angle and U-shaped designs.
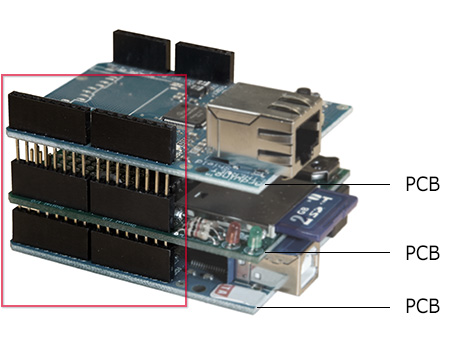
How do we stack PCBs?
Amid the trends of miniaturization, transitioning to light weight and high speed, designers often face many constraints, both mechanically, and electrically. Greenconn offers various solutions to accommodate all stacking options.
Vertical - Parallel, Mezzanine - Both connectors are in a vertical orientation. This allows a PCB to be stacked on top of another, minimizing the surface area as a result.
Horizontal - 180 Degree, Coplanar, Edge-to-Edge - Both connectors are in a horizontal orientation. From the design standpoint, this keeps the mating centerline low profile to the PCBs.
Perpendicular - Motherboard to Daughterboard - Connectors are perpendicular to one another. This is commonly seen in hard drive applications where many "Daughterboards” are stacked onto one motherboard, allowing the data storage space to be efficiently expanded.
Here are some advantages of stacking PCBs:
The design can be modularized into smaller PCBs and the PCBs can be connected using BTB
connectors later on during assembly. This not only improves the design process but
also allows modifications to be made easily.
From the assembly perspective, it can improve the manufacturability of the product,
by operating with smaller PCBs rather than one large PCB.
Overall, properly stacking PCBs in layers can enhance the EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) of the design.
What are connector pitches?
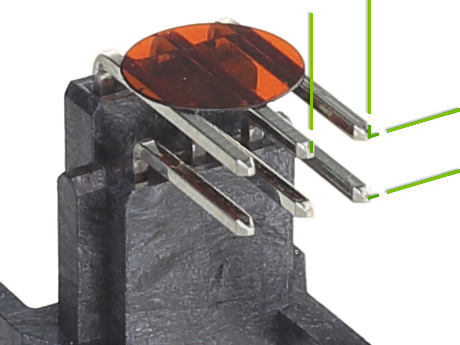
Connector Pitch is the measurement from the center of one contact to the center of the next contact. When a connector has multiple rows, the pitch in each row and the pitch between rows may be different.
There are numerous factors for the hardware designer to consider when choosing the correct connector pitch:
- Space Constraints - The smaller the pitch, the smaller the connector can be. In addition, smaller pitch can offer a greater number of contacts within the same space.
- Electrical Parameter – Pitch size has a positive correlation to electrical specifications such as current rating and dielectric withstanding.
-
Other Physical Constraints - Depending on the design,
Greenconn offers numerous low-profile connector options across all pitches.
We also accept customization requests.
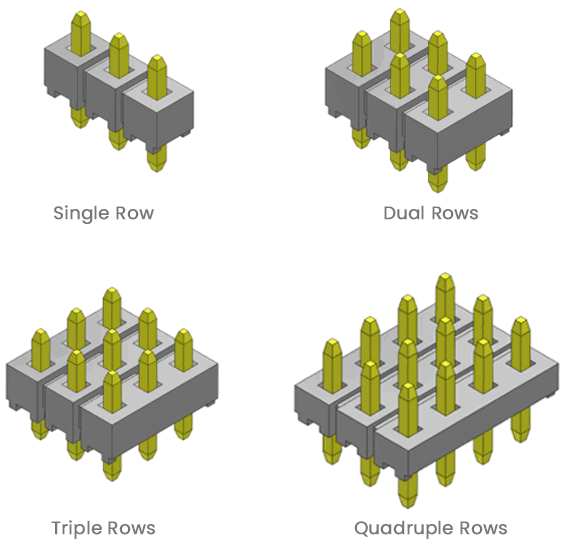
Greenconn’s board-to-board connectors are available in the following rows:
Rows:
Greenconn offers headers and recepticles in single, double, triple, and quadruple row configurations. Single and dual rows are popular choices, while triple and quadruple rows are offered in a smaller number of pitch and style options.
What are the Connector Contact Materials and Plating?
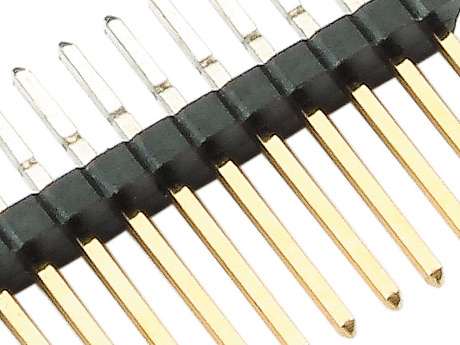
Base Material
Our connectors typically use a copper alloy as the base material for their contacts (pins). However, different alloy materials offer various levels of conductivity performance and physical endurance.
Here’s a comparison of the common base materials offered at Greenconn:
-
Brass
- Lowest cost
- Good strength and spring properties
- Good conductor
-
Phosphor Bronze
- High level of strength and conductivity
- Superior elasticity
- Excellent fatigue resistance
-
Berylium Copper (Be-Cu)
- High level of strength and conductivity
- Highly expansive
Plating
Plating affects the connector’s performance, life cycle, quality, and cost.
Plating involves two parts: underplating and finish plating:
Under-plating
Underplating is used to enhance the performance. This process forms an internal diffusion barrier (Zn and Cu through gold) and prevents pollutants from reacting with base metals. It also acts as a medium to help the finish plating adhere to the base material. Nickel is the most common and important under-plate in current use for these reasons:
- Corrosion resistance
- Wear resistance
- Solderability
Finish plating
Finish plating is the second step of the plating process that helps strengthen the electrical conductivity. There are various options for finish plating, depending on the design requirements and budget.
I. Gold Plating:
- Excellent resistance to corrosion
- Excellent conductivity and low electrical resistance
- High cost
II. Tin Plating:
- Excellent solderability and conductivity
- Low durability and can form an oxide film
- High cost
*Tin can be further characterized as bright tin or matte tin.
A. Bright Tin
Bright tin can be easily identified by its glossy texture. It works well against corrosion, while sacrificing its solderability.
B. Matte Tin
Matte tin, as opposed to bright tin, has a dull texture, which is not as appealing as the bright tin.
However, it offers a good level of protection against corrosion without sacrificing its solderability.
III. Selective Gold-Tin Plating
This type of plating offers tin plating on the tail and gold plating on the contact area. It offers a good balance between the advantages of gold and the lower cost of tin.
IV. Others
Greenconn also offers more than just the standard gold and tin plating options. For more information on plating, please contact us as https://www.Greenconn.com/en/contact.htm .
Plastic Insulators
Plastic
Insulators are fundamental to board-to-board connectors. They are used to hold the conductors, or pins, together to create the desired shape of the connectors. Different insulators also perform differently regarding to their strength, weatherability, and chemical resistance.
Here are some of the plastic insulators Greenconn offers that can be used in a variety of applications:
Common Insulators
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
- Excellent dielectric strength under high temperatures (230°C) and high humidity
- Great formability with low shrinkage rate
- Low flammability
- Great impact strength
- Available in Halogen-free options
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Good impact toughness even at low temperatures
- Great wear resistance against rough surfaces
- Shiny appearance
- Economical
Insulators for High temperature(SMT-Grade)
High Performance Polyamide (PA 46 , PA 6T)
- Temperature rating, PA46 290°C, PA6T 320°C
- Good elongation
- High rigidity, even at high temperatures
- Available in Halogen-free options
Liquid-Crystal Polymer (LCP)
- Temperature rating between 290-320°C
- Great dimensional stability and weatherability
- Chemically inactive
- Great moldability, popular for designs requiring high precision and low flammability (UL 94V-0)
- Available in Halogen-free options
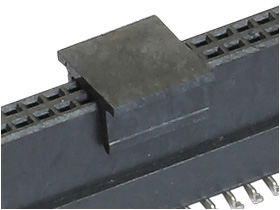
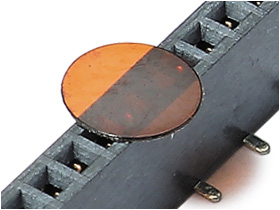
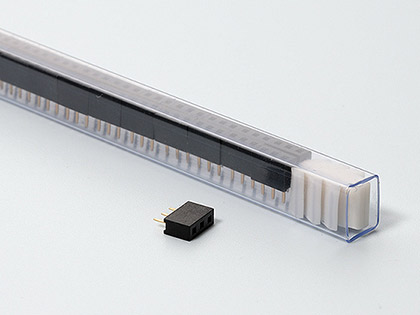
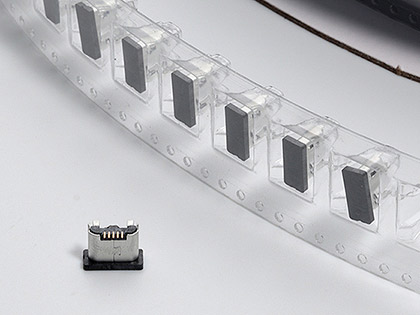
Packaging Options
Packaging is critical in its ability to protect the goods during transportation and allow the receiver to open at ease.
Here are the various packaging options offered for Board-to-Board connectors:
- Bulk (PE bag or small box)
- Trays
- Tubes
- Tubes with Pick and Place (P&P) Cap or Kapton tape
- Tape and Reel (T&R) with Pick and Place (P&P) Cap or Kapton tape
- Tape and Reel (T&R)
- Custom packaging