How Wire-to-Wire Connectors Work & Their Applications in Modern Electronics
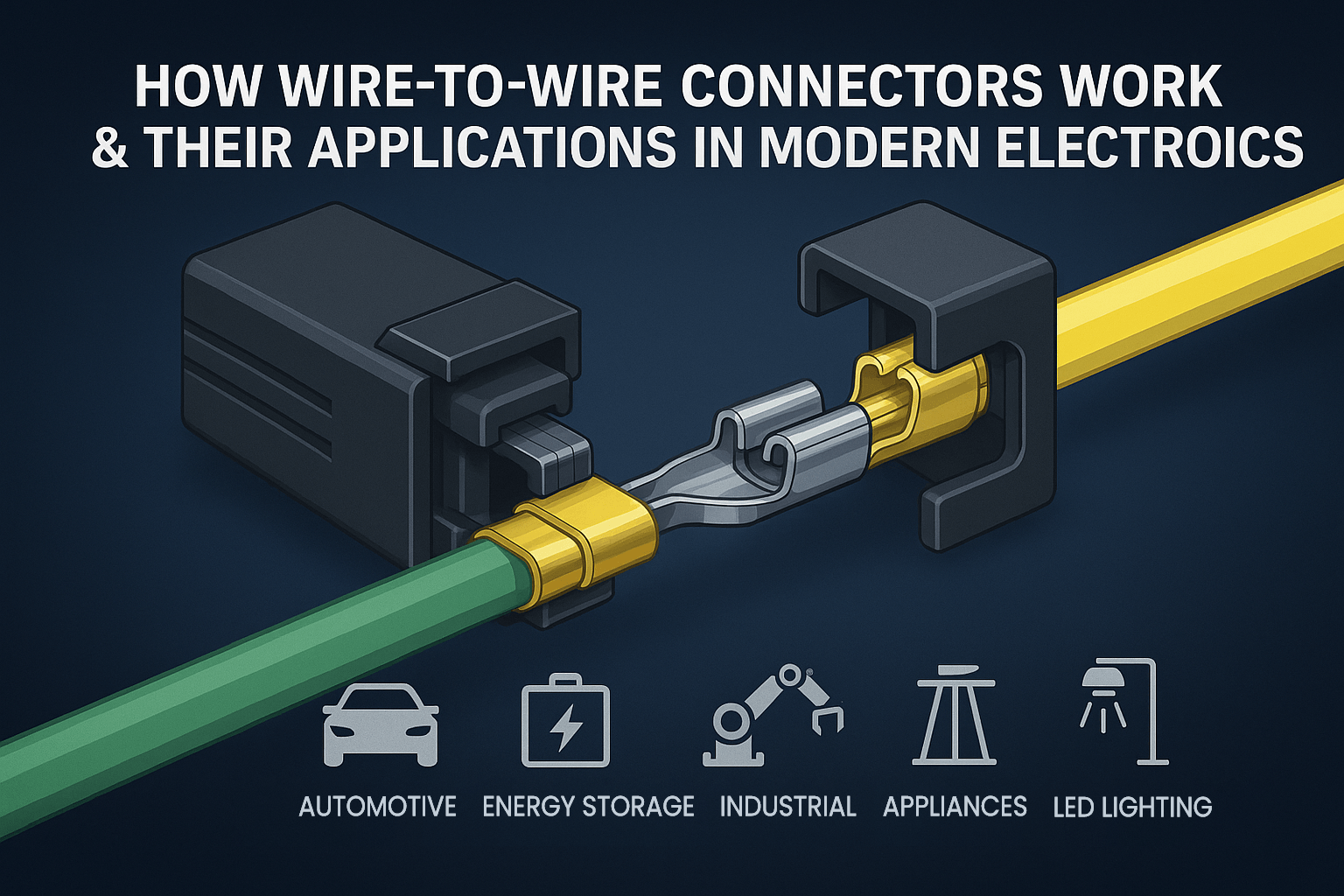
Wire-to-wire connectors are essential components used to directly join two separate conductors without relying on a PCB. They are widely adopted in environments requiring modularity, high-reliability interconnects, and fast assembly. Their construction integrates metal terminals, plastic housings, locking mechanisms, and, in some cases, environmental seals.
1. How Wire-to-Wire Connectors Work
Terminal Design
The core of a wire-to-wire connector is its stamped and formed metal terminal (often copper alloy with tin or gold plating), which ensures low contact resistance and long-term reliability under current load.
Crimping or IDC Connection
Wires are connected to terminals via precision crimping or insulation displacement contact (IDC), eliminating soldering and reducing process variability. These are governed by IPC/WHMA-A-620 Class 2 or 3 standards.
Mating & Retention System
Secure mating is achieved via mechanical locks, often reinforced with TPA (Terminal Position Assurance) designs that prevent incomplete insertion or terminal back-out under vibration.
Sealing & Environmental Protection
In harsh applications, waterproof versions incorporate IP-rated seals (e.g., IP67) and hydrophobic materials to prevent moisture ingress and dust accumulation.
2. Typical Applications of Wire-to-Wire Connectors
- Automotive Wire Harnessing: Powertrain sensors, door modules, and lighting systems—requiring vibration resistance and thermal endurance.
- Energy Storage Systems: Battery-to-BMS or high-voltage modules—demanding flame retardancy and current-carrying capability.
- Industrial Automation & Robotics: Motor drives, I/O modules, PLC connections—needing signal integrity and EMI shielding.
- Consumer & Home Appliances: Modular connections in white goods—emphasizing cost-effectiveness and high-volume manufacturability.
- LED Lighting Systems: Driver-to-fixture connections—requiring UV resistance and long-term outdoor performance.
3. Trends in Wire-to-Wire Connector Design
As device integration increases, wire-to-wire connectors are evolving toward higher density, miniaturization, modularity, and enhanced environmental adaptability. For example, Greenconn's waterproof wire-to-wire series incorporates multi-row pin configurations, anti-mating failure designs, and UL94V-0 flame-retardant materials to meet the complex requirements of new energy and industrial applications.