Choosing the Right Shielding Material for Connectors
In today's high-frequency electronic systems, controlling electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk is essential to maintaining signal integrity. Selecting the right shielding material is a critical part of connector design that directly impacts system reliability and performance across automotive, industrial, and consumer applications. Here are key factors to consider when choosing shielding materials:
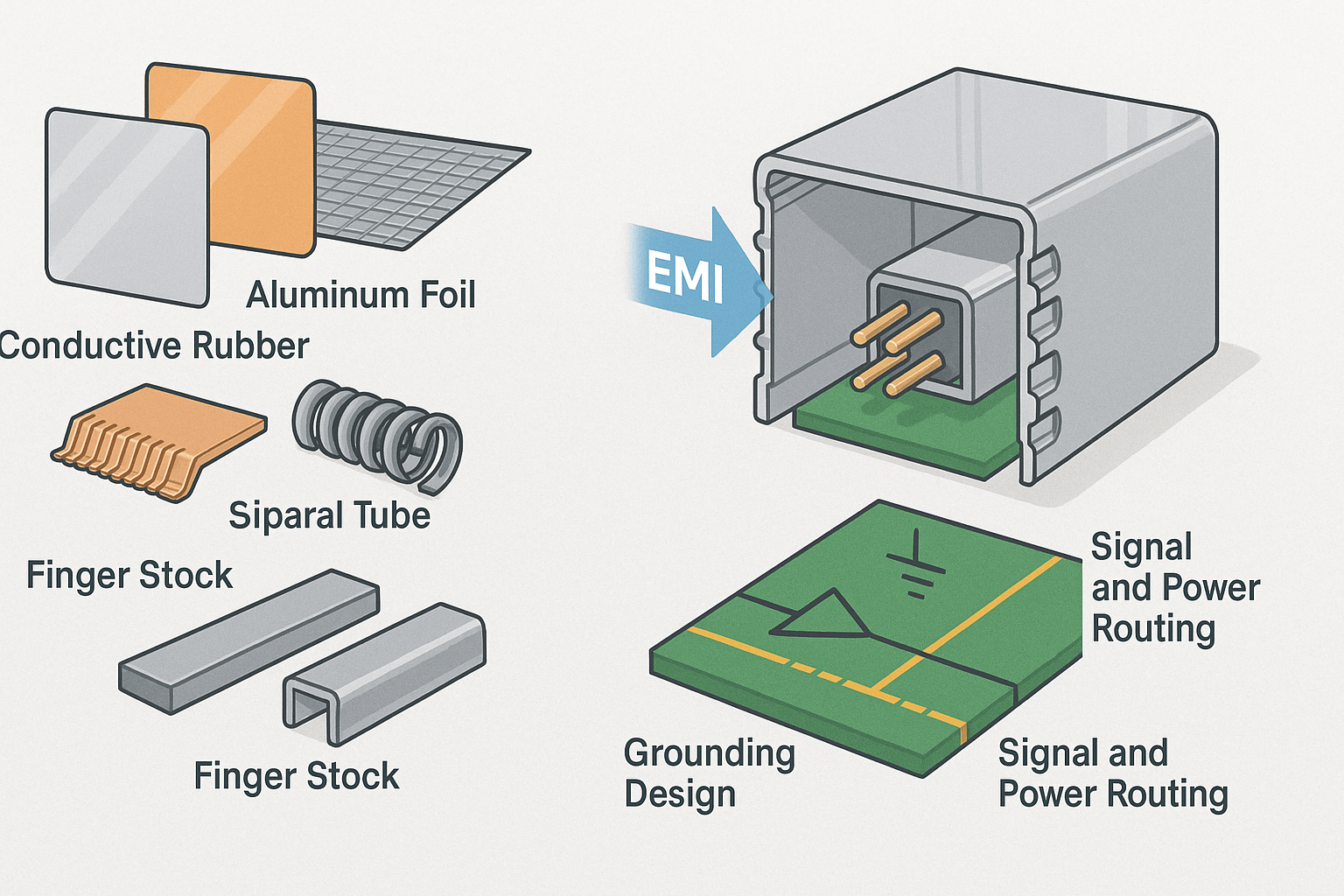
- EMI Shielding Materials
Materials like copper or aluminum foil offer excellent conductivity and are widely used for effective EMI protection. - Conductive Rubber & Metal Mesh
These provide both electromagnetic shielding and environmental sealing, ideal for high-frequency or outdoor applications. - Finger Stock & Spiral Tubes
Beryllium copper finger stock and metal spiral tubes combine high shielding effectiveness with environmental durability—suited for demanding use cases. - Elasticity & Conductivity
Good elasticity and continuous conductivity ensure reliable shielding performance under varying mechanical and environmental conditions. - Environmental Resistance
For harsh conditions, choose materials resistant to humidity, temperature changes, and mechanical stress like vibration or corrosion. - Shielding Structure
Beyond materials, structure matters. For example, Greenconn's ZenShield® series uses a 360-degree shielding design to reduce EMI emissions. - Grounding Design
Proper grounding of the shielding layer is vital. A low-impedance path to ground, preferably with multi-point grounding, improves EMI suppression. - PCB Layout
Optimize trace spacing, ground plane design, and signal isolation (e.g., analog vs digital) to minimize crosstalk at the board level. - 3W Rule
As a baseline, maintain a spacing of three times the trace width between signal lines. Greater spacing may be needed in unshielded designs. - Signal & Power Routing
Avoid parallel or overlapping signal and power traces. Use orthogonal routing and ground isolation to reduce mutual interference.
By considering material properties, shielding structures, grounding strategies, and layout design, engineers can significantly reduce crosstalk and enhance EMI performance. This leads to more reliable, high-integrity connector solutions across modern electronics.